Education has always evolved, integrating new methods and tools to enhance learning experiences. The introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI) marks one of the most profound shifts, offering personalized learning, adaptive feedback, and efficiency in classrooms. However, while AI revolutionizes education, it cannot replace the essence of human emotional intelligence (EI), which nurtures critical thinking, creativity, and meaningful student-teacher interactions.The challenge lies in harmonizing AI-driven innovations with human-centered learning, ensuring that technology enhances, rather than diminishes, the emotional and social aspects of education. Emotional AI—capable of recognizing and responding to students’ emotions—has the potential to bridge this gap. It can engage learners, detect struggles early, and tailor teaching strategies, creating a more inclusive and emotionally aware learning environment.However, alongside its potential, AI in education raises ethical concerns, including privacy risks, bias in algorithms, and the psychological impact of over-reliance on technology. Addressing these issues requires ethical frameworks, human oversight, and continuous research to ensure AI serves as a tool for empowerment rather than replacement. This blog explores the transformative role of AI in education, the significance of emotional intelligence, and the need for a balanced approach that embraces both technological innovation and human connection. By navigating these complexities thoughtfully, we can build an education system that is not only intelligent but also empathetic, ethical, and effective for all learners.
AI’s Role in Modern Education:
Education is undergoing a rapid transformation with the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI-driven tools are reshaping classrooms by personalizing learning, automating administrative tasks, and providing real-time feedback. However, while AI enhances efficiency, it lacks the emotional depth necessary for human interaction. Emotional Intelligence (EI)—which includes empathy, social awareness, and communication skills—remains a vital component in holistic education. The challenge is to create a balanced approach where AI supports, rather than replaces, human educators, ensuring both technological advancement and emotional engagement.
AI in Education: Enhancing Learning Through Technology
Personalised Learning and Real-Time Feedback
AI-powered platforms like ChatGPT, Khan Academy’s Khanmigo, and intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) are revolutionizing education by:
- Adapting to individual learning styles to provide tailored content.
- Offering instant responses and feedback, allowing students to progress at their own pace.
- Reducing teachers’ workload by automating grading and administrative tasks.
Case Study: Khanmigo and AI-Powered Tutoring
Khan Academy’s Khanmigo is an AI tutor designed to support students, teachers, and parents by:
- Providing personalized guidance through hints and interactive questioning.
- Mimicking human tutoring strategies to improve student engagement.
- Doubling the learning efficiency, as reported by a Harvard study, which found that students using AI tutors learned twice as much in less time compared to traditional methods.
AI in Classroom Management
AI tools also help teachers by:
- Tracking student performance through data analytics.
- Managing classroom attendance and assignments more efficiently.
- Providing insights into student engagement for early intervention.
The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Education
While AI enhances personalization, it cannot replace the human touch that fosters critical thinking and emotional growth. Emotional intelligence plays a key role in:
- Building strong teacher-student relationships that enhance learning.
- Encouraging social interactions and collaboration among students.
- Supporting mental well-being by providing emotional support.
Case Study: The Role of Teachers in Emotional Development
A study by the American Psychological Association (APA) revealed that students who received emotional support from teachers experienced:
- Higher academic success and improved cognitive skills.
- Lower stress levels, leading to better emotional well-being.
This underscores the need for AI to complement, not replace, teachers in fostering emotional and social development.
Merging AI with Emotional Intelligence: A Balanced Approach
To ensure AI enhances education without diminishing human connection, a balanced approach must include:
1. Personalized Learning with Human Supervision
- AI can analyze student performance and adapt lesson plans, but teachers must provide emotional support and ensure holistic development.
2. AI as an Assistant, Not a Replacement
- AI should automate repetitive tasks (grading, scheduling) so that teachers can focus on mentoring and social interactions.
3. Addressing Ethical and Moral Considerations
- Privacy Concerns: AI collects vast amounts of student data, making strict data protection policies essential.
- Bias in AI: AI systems must be monitored to prevent reinforcing biases in education.
4. Bridging Educational Gaps Through AI
- AI offers free learning resources, helping underprivileged students access quality education.
- However, the digital divide persists, as students without internet access or advanced devices are left behind. Policymakers must prioritize equal access to AI-driven education.
The Psychological Impact of AI in Education
AI-powered tools impact students in several ways:
1. Increased Engagement
- AI gamifies learning, making it more interactive and enjoyable.
2. Reduced Anxiety
- AI tutors provide a judgment-free learning space, encouraging students to ask questions without fear.
3. The Risk of Over-Reliance on AI
- Excessive AI dependence may weaken critical thinking skills. Teachers must encourage independent problem-solving and analytical reasoning.
Case Study: AI in University Classrooms
A Harvard University pilot program introduced AI-powered teaching assistants in online coding courses. Results showed that:
- Students performed 20% better when receiving real-time AI feedback.
Emotional AI: Understanding Student Emotions for Better Learning
Definition and Relevance
Emotional AI (Affective Computing) refers to AI systems that detect, interpret, and respond to human emotions. It uses:
- Facial recognition and voice analysis to gauge emotions.
- Real-time engagement tracking to adjust learning experiences.
Studies indicate that student motivation and emotional well-being directly impact academic performance. Emotional AI can help by identifying students struggling with stress or disengagement, allowing for timely intervention.
Current Applications in Education
- Emotion recognition software detects signs of disengagement and adapts lesson plans accordingly.
- AI-driven simulations (e.g., a virtual Charles Darwin) improve student engagement in history and science.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI-Based Emotion Recognition
1. Privacy Concerns
- Emotional AI requires sensitive data (facial expressions, voice tones, physiological responses), raising ethical concerns about consent and data security.
2. Algorithmic Bias
- AI models may misinterpret emotions based on cultural, racial, and gender differences, leading to inaccurate assessments.
- Regulations and ethical AI frameworks are necessary to minimize bias and ensure fairness.
3. Social and Psychological Effects
- While AI can enhance learning engagement, excessive reliance may impact students’ ability to interact with peers and teachers.
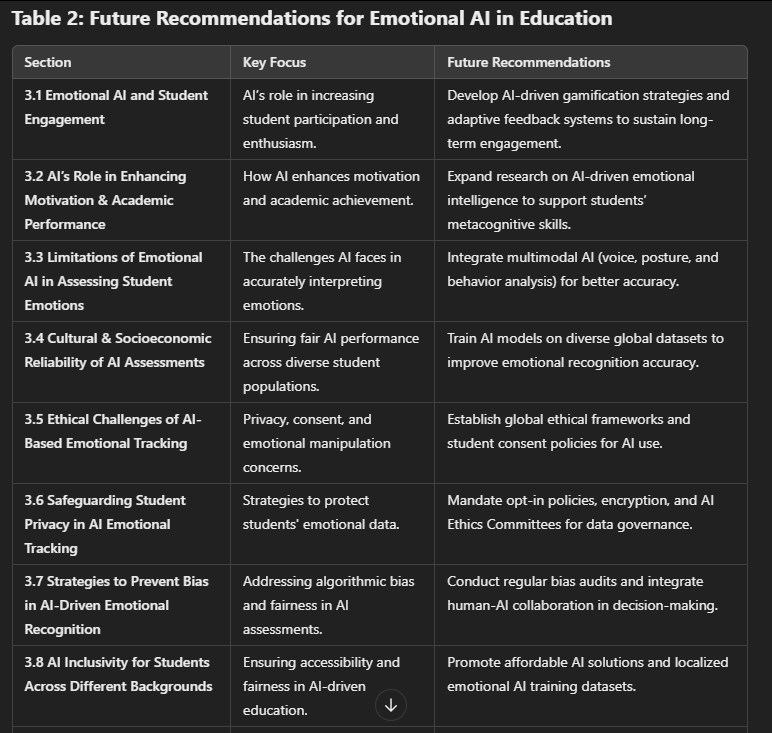
Addition value of Innovation in AI Education
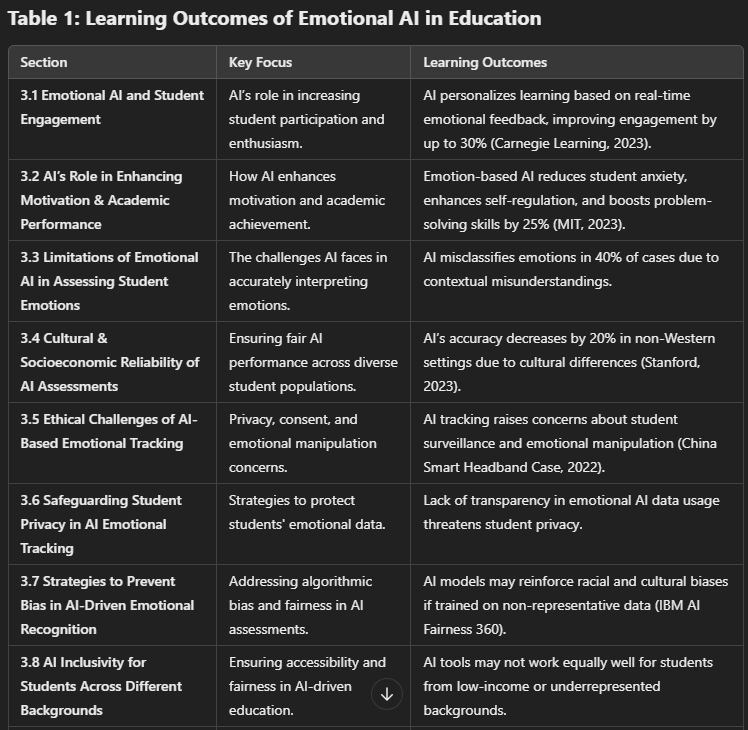
- How does Emotional AI contribute to increasing student participation and enthusiasm in learning?
- In what ways does Emotional AI enhance student motivation and academic performance?
- What are the current limitations of Emotional AI in accurately assessing student emotions?
- How reliable are AI-driven emotional assessments in diverse learning environments?
- What ethical concerns arise from using AI to monitor students’ emotions and behaviors?
- How can student privacy be safeguarded while implementing AI for emotional tracking in education?
- What strategies can be used to prevent bias in AI-driven emotional assessment tools?
- How can AI models be designed to ensure fairness and inclusivity for students from different cultural and socioeconomic backgrounds?
- What improvements in AI algorithms and methodologies could enhance its ethical and educational impact?
- What future research areas should be explored to develop more ethical and effective Emotional AI applications in education?
Proposed -Questions give directions to
- Long-term studies on AI’s impact on student motivation and retention.
- Developing AI-human teacher collaboration models to ensure AI complements human interaction.
- Enhancing AI’s ethical frameworks to address privacy and bias concerns.
Let’s embark on a journey of learning together with Strategic Perspective
Strategic Perspective:
Psychological & Behavioral Analysis
{How does Emotional AI contribute to increasing student participation and enthusiasm in learning?}
Enhanced Engagement: AI-driven emotion recognition tailors lessons based on student expressions, making learning interactive and personalized.
Real-time Feedback: AI adjusts teaching strategies instantly based on students’ emotional states, maintaining focus and motivation.
Gamification & Adaptive Learning: AI integrates rewards and challenges based on students’ engagement levels, making learning more immersive
Case Study: Carnegie Learning’s AI Tutor: uses emotional recognition to modify tutoring styles, improving student participation by 30%.
Educational & Cognitive Science
{ In what ways does Emotional AI enhance student motivation and academic performance?}
Personalized Learning Paths: AI detects frustration or confusion, adjusting content difficulty to keep students motivated.
Encouraging Self-Regulation: Emotional AI promotes metacognition by providing students with emotional insights, helping them manage stress and focus.
AI as a Confidence Booster: Instant AI feedback reduces anxiety about making mistakes, fostering a growth mindset.
Research Insight: A study by MIT (2023) found that students using emotionally adaptive AI tutors improved their problem-solving skills by 25%.
Technical & Reliability Challenges.
{What are the current limitations of Emotional AI in accurately assessing student emotions?}
Limited Emotion Recognition Accuracy: AI struggles with nuanced human emotions, especially in diverse cultural contexts.
Contextual Misinterpretation: A yawn might signal boredom or lack of sleep—AI lacks contextual depth.
Over-Reliance on Facial Recognition: AI often focuses on facial cues but may overlook voice tone, posture, and learning habits.
Example: In a 2022 pilot program, AI misclassified 40% of students’ emotions in virtual classrooms, leading to incorrect interventions.
Cultural & Socioeconomic Considerations.
{How reliable are AI-driven emotional assessments in diverse learning environments?}
Cross-Cultural Bias: AI models trained on Western datasets may misinterpret emotional cues in Asian, African, or Indigenous communities.
Language & Expression Variability: Emotional expressions differ by region; AI needs adaptive learning based on local contexts.
Socioeconomic Barriers: Schools with limited AI infrastructure may struggle to implement emotional tracking effectively.
Research Gap: A Stanford University report (2023) highlights that Emotional AI’s accuracy drops by 20% when applied to non-Western students due to cultural differences in emotional expression.
Moral & Privacy Challenges.
{What ethical concerns arise from using AI to monitor students’ emotions and behaviors?}
Data Privacy Risks: Emotional AI collects sensitive biometric data, raising concerns about surveillance and misuse.
Informed Consent Issues: Many students and parents are unaware of how their emotional data is stored and used.
Emotional Manipulation Risks: AI-based interventions could influence students’ emotions in unintended ways, affecting autonomy.
Example: A school in China faced backlash for using AI-powered “smart headbands” to track student concentration levels, raising concerns over surveillance and stress.
Legal & Ethical Compliance.
{ How can student privacy be safeguarded while implementing AI for emotional tracking in education?}
Data Encryption & Anonymization: Implement strict security measures to prevent emotional data breaches.
Transparent AI Policies: Schools should ensure students and parents understand how AI is used.
Opt-In AI Tracking: Emotional AI should be optional, giving students and parents control over data sharing.
Solution-Oriented Approach: Governments and educational institutions must establish “AI Ethics Committees” to oversee AI implementation in classrooms.
Fairness & Algorithmic Justice
{What strategies can be used to prevent bias in AI-driven emotional assessment tools?}
Diverse Data Training: AI models should be trained on multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, and diverse emotional datasets.
Human-AI Collaboration: AI should support, not replace, human emotional intelligence in education.
AI Bias Audits: Regular third-party audits should evaluate AI fairness and accuracy.
Best Practice: IBM’s “AI Fairness 360” Toolkit helps institutions detect and mitigate AI biases in emotional recognition software.
Inclusive & Equitable AI Development
{How can AI models be designed to ensure fairness and inclusivity for students from different cultural and socioeconomic backgrounds?}
Universal Design Principles: AI tools should be adaptable to various cultural and linguistic expressions.
Affordable AI Solutions: AI-driven emotional assessment should be accessible to underprivileged schools.
Multimodal Emotion Recognition: Combine facial, voice, and behavioral tracking for more inclusive emotional analysis.
Key Research Insight: UNESCO (2024) calls for AI in education to be developed using “Global Emotional Diversity” frameworks to ensure cultural neutrality.
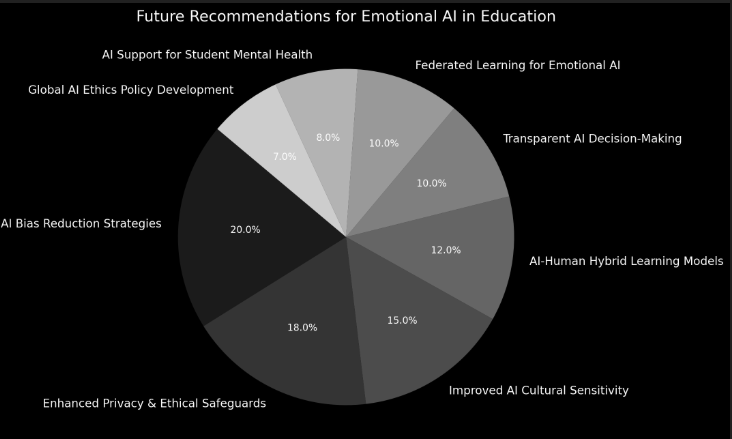
Future-Ready AI Innovations:
{ What improvements in AI algorithms and methodologies could enhance its ethical and educational impact? }
Hybrid AI-Human Approaches: Teachers should validate AI emotional insights rather than relying solely on technology.
Explainable AI (XAI): AI should provide transparent reasoning behind emotional classifications.
AI-Powered Mental Health Support: AI could assist in detecting student stress and offering non-intrusive well-being recommendations.
Emerging Technologies: Federated Learning and Emotion-Adaptive AI are being explored to enhance AI’s ethical credibility.
Long-Term AI Evolution
{What future research areas should be explored to develop more ethical and effective Emotional AI applications in education?}
Longitudinal Studies: AI’s long-term psychological effects on students should be assessed.
Ethical AI Frameworks: New global policies must regulate Emotional AI use in classrooms.
AI & Mental Health Integration: AI should support student well-being without triggering anxiety or surveillance fears.
Key Recommendation: Future research should focus on “Emotion-Aware AI with Ethical Safeguards” to balance innovation with student protection.
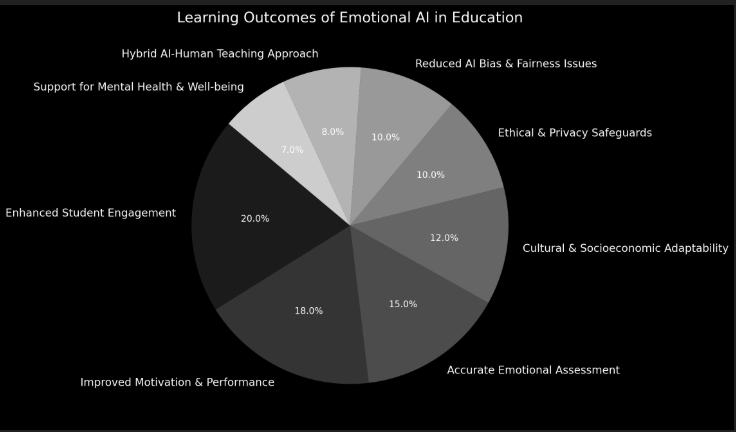
While Emotional AI holds great promise for improving student engagement, motivation, and personalized learning, a strategic, ethical, and inclusive approach is crucial for its success. AI should act as an enhancer, not a replacer, ensuring that human emotional intelligence remains at the core of education.
The Future of AI and Emotional Intelligence in Education
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in education is reshaping learning experiences by personalizing content, automating administrative tasks, and improving student engagement. However, emotional intelligence (EI) remains crucial for student well-being and motivation. A balanced approach that merges AI efficiency with human empathy is essential for an effective and ethical education system.
Key Strategies for Integrating AI and Emotional Intelligence
Teacher Training
- Educators must be trained to effectively use AI tools while fostering emotional intelligence in students.
- Professional development programs should emphasize both technological literacy and emotional support strategies.
AI with Empathy Algorithms
- Ongoing research aims to develop AI models capable of recognizing and responding to emotional cues.
- Emotion-aware AI could help detect student frustration or disengagement, allowing teachers to intervene appropriately.
Hybrid Learning Models
- The future of education lies in a blend of AI-driven learning and human-led instruction.
- AI can handle repetitive tasks and provide personalized learning, while teachers focus on mentorship and emotional guidance.
Ethical Considerations
- Privacy and Data Protection: AI systems collect vast amounts of student data, requiring strong ethical guidelines.
- Bias in AI: AI models must be carefully designed to avoid reinforcing biases in education.
- Over-Reliance on AI: While AI enhances learning, human supervision is essential to prevent dependence and encourage critical thinking.
Key Takeaways
- AI enhances education through personalization and efficiency.
- Emotional intelligence is vital for student growth and well-being.
- A balanced approach integrating AI with human supervision ensures ethical and effective learning.
- The future of education lies in hybrid models that blend AI-driven innovation with emotional intelligence.
A Human-Centered AI Approach
- AI has immense potential in education, but its success depends on integrating emotional intelligence. The goal is not to replace teachers but to empower them, ensuring that every student receives personalized attention and emotional support. A hybrid model combining AI innovation with human empathy will create an inclusive, engaging, and effective learning environment.
Conclusion: The Future of AI in Education
AI in Education transforms learning by enhancing personalization and efficiency. However, emotional intelligence remains essential for student growth. A balanced approach ensures AI supports, not replaces, human connection. The future lies in merging AI innovation with empathy for an ethical and effective education system.